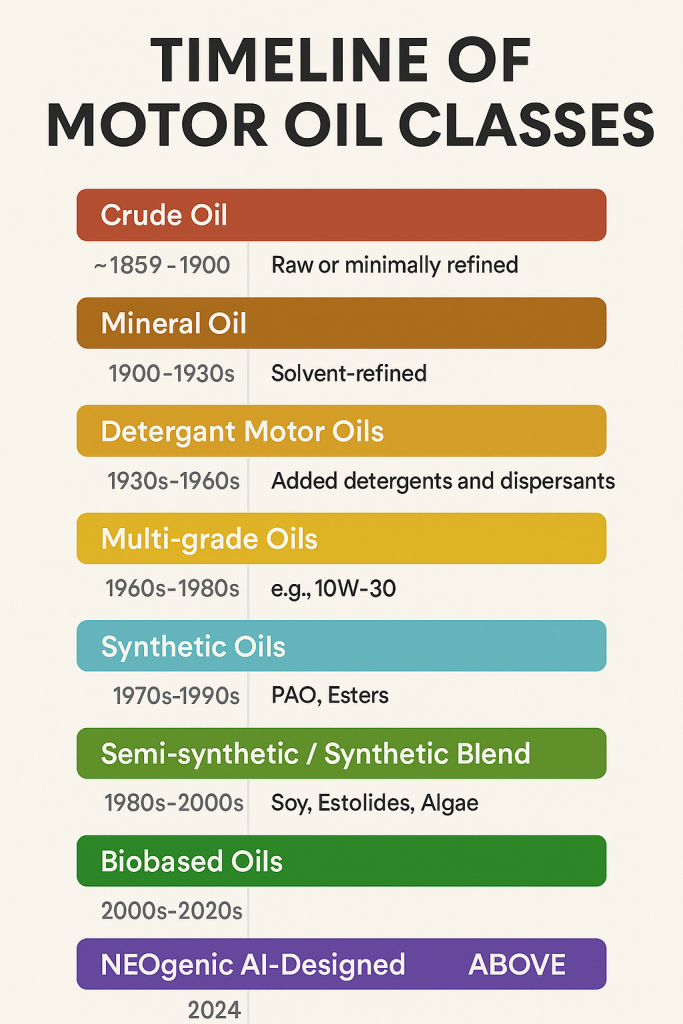
🌱 Class-by-Class Breakdown:
1. Crude Oil Lubricants
- Years: ~1859–1900
- Issues: Dirty, non-additized, highly variable
- Use: Steam engines, early gasoline engines
- Replaced by: Refined mineral oils

2. Mineral Oils
- Years: ~1900–1960s (base for many blends still)
- Base Stock Group: Group I
- Advantages: Cheap, readily available
- Limitations: Low oxidation and thermal stability
- Still used?: Yes, in budget or industrial lubricants
3. Additized Detergent Oils
- Years: 1930s–1970s
- Milestone: First API classifications (SA–SD)
- Innovation: Added ZDDP and detergents
- Superseded by: Higher-spec API oils (SE, SF…)
4. Multi-grade Oils
- Years: 1960s–now
- Breakthrough: Flow in cold and hot temps (e.g., 10W-30)
- Still used?: Yes, almost all oils today are multi-grade

5. Full Synthetic Oils (Group IV & V)
- Years: 1970s–present
- Example: Mobil 1 (1972)
- Features: Uniform molecules, high VI, low pour point
- Limitations: Expensive to produce
- Use: Performance, aviation, racing, extreme weather
6. Synthetic Blends (Group II/III + IV/V)
- Years: 1980s–present
- Popularized by: Budget-conscious markets
- Compromise: Some benefits of synthetics at lower cost
7. Hydrocracked “Synthetic” (Group III)
- Years: Late 1990s–present
- Tech: Gas-to-liquid (GTL), severe hydrocracking
- Marketing Controversy: Labeled “synthetic” in U.S. after Mobil v. Castrol
- Use: Widely sold as full synthetic in retail stores
8. Biobased and Biodegradable Oils
- Years: ~2005–present
- Feedstocks: Soy, canola, estolides, algae
- Benefits: Renewable, low toxicity, biodegradable
9. 🧬 NEOgenic Oils (ABOVE.energy) – AI-Crafted Oils
- Years: 2024–present
- Origin: Selected plant & algae strains with tailored polarity and molecular chains
- Technology:
- AI-selected base oils by species/genetic traits
- AI-designed additive systems for specific engines
- Molecular tuning for honing patterns, ring pressure, coatings
- Eco Impact: Designed to be carbon-negative, biodegradable, engine-customized
- Revolution: Not synthesized from crude—built for performance from renewable biology

📈 Overlap and Transitions
- Many classes overlap due to cost, geography, and regulation.
- Biobased and NEOgenic oils are not yet dominant, but are rapidly growing due to:
- ESG regulations
- Racing & high-performance engine demand
- Environmental branding and carbon offset goals
- Friction reduction from absolute zero reasoning agents and simulations

Leave a Reply